Flagella
Most prokaryotes are motile by swimming, and this function is typically due to a structure called the flagellum. The plural form of this word is flagella which means whip. Bacterial flagellum is a threadlike locomotor appendages extending outgrowth from the plasma membrane and cell wall.
Bacterial flagella are thin, rigid structures, about 20 nm across and up to 15-20 μm long.Flagella are so thin that a single flagellum can be seen with the light microscope only after being stained with special stains that increase their diameter. However, flagella are easily seen with the electron microscope.
Best safe and secure cloud storage with password protection
Get Envato Elements, Prime Video, Hotstar and Netflix For Free
Best Money Earning Website 100$ Day
#1 Top ranking article submission website
Arrangement of flagella
- Atrichous: Bacteria have no flagellum. e.g. Micrococcus corchorii.
- Monotrichous: (mono means one; trichous means hair)Bacteria have one flagellum; if it is located at an end, It is said to be a polar flagellum. e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Amphitrichous: (amphi means on both sides) Bacteria have a single flagellum or clusters at each pole. e.g. Aquaspirillum serpens.
- Lophotrichous: (lopho means tuft) Bacteria have a cluster of flagella at one end. e.g. Rhodospirillum photometricum.
- Peritrichous: (peri means around) Flagella are spread fairly evenly over the whole surface of bacterial cell. e.g. Proteus vulgaris.

Structure
Flagella are not straight but are helical. When flattened, flagella show a constant distance between adjacent curves called the wave and this wave length is charecteristics for the flagella of any given species. A flagella consists of several components an moves by rotation, much like a propellar of a boat motor. The base of the flagellum is structurally different from the fillament. There is a wide region at the base of the fillament called the hook. The hook consist of a single type of proteins and connects the fillament to the motor portion of the base.
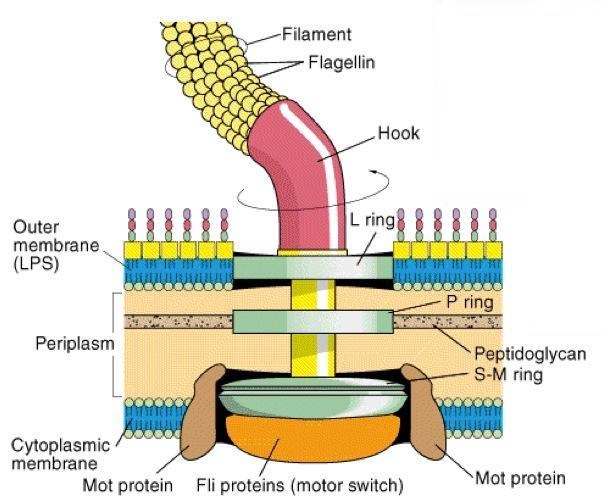
Transmission electon microscope(TEM) studies have shown that the bacterial flagellum is composed of three parts.
- Filament: The longest and most obvious portion is the flagellar filament, which extends from the cell surface to the tip.
- Basal body: The basal body anchors the flagellum to the cell wall and plasma membrane.
- Hook: A short, curved segment consists of different protein, the flagellar hook links the filament to its basal body and acts as a flexible coupling.The motor is anchored in the cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall. The motor consists of a central rod that passes through a series of rings.
 Plantlet The Blogging Platform of Department of Botany, University of Dhaka
Plantlet The Blogging Platform of Department of Botany, University of Dhaka






So much informative. Nice article.
Thanks Bari
Keep up the incredible work! I can’t wait to see what you write next.
It means the world to us to hear such positive feedback on our blog posts. We strive to create valuable content for our readers and it’s always encouraging to hear that it’s making an impact.
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
Fantastic site. Lots of helpful information here. I am sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks for your effort!
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
I do believe all the ideas you’ve presented for your post. They are really convincing and will certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are too short for novices. May just you please lengthen them a little from subsequent time? Thanks for the post.
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to more added agreeable from you! By the way, how could we communicate?
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site, how could i subscribe for a blog site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
My brother suggested I might like this blog. He was totally right. This post actually made my day. You can not imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to assert that I get actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently fast.
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
Fantastic site. A lot of helpful info here. I’m sending it to some buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks on your sweat!
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
Fantastic site. A lot of helpful info here. I’m sending it to some buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks on your sweat!
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
Hey there, You have done a fantastic job. I will certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this site.
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again.
obviously like your web-site but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand I’ll certainly come back again.
Thank you so much for your Valuable comment. We wish to hear from you again. And we will try our best to focus on the spellings too!
I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will moviesbox.net
Thanks, I have just been looking for information about this subject for a long time and yours is the best I’ve discovered till now. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the supply?
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly articles I’d state. That is the very first time I frequented your website page and up to now? I surprised with the research you made to make this actual submit amazing. Wonderful task!
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
I just could not leave your web site before suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard information a person supply to your visitors? Is gonna be again steadily in order to check up on new posts.
Just wish to say your article is as surprising. The clearness in your post is just cool and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the enjoyable work.
I do agree with all the ideas you have introduced on your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are very short for newbies. May just you please prolong them a little from subsequent time? Thank you for the post.
Normally I do not read article on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do so! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thanks, quite great post.
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this post is amazing, great written and include almost all significant infos. I would like to look extra posts like this.
I do agree with all the ideas you have introduced on your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are very short for newbies. May just you please prolong them a little from subsequent time? Thank you for the post.
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly articles Id state That is the very first time I frequented your website page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to make this actual submit amazing Wonderful task
What i do not realize is in fact how you are no longer actually much more wellfavored than you might be right now Youre very intelligent You recognize thus considerably in relation to this topic made me in my view believe it from numerous numerous angles Its like men and women are not fascinated until it is one thing to do with Lady gaga Your own stuffs excellent All the time handle it up
Your blog post had me hooked from the very beginning!
Your writing style is so engaging and easy to follow I find myself reading through each post without even realizing I’ve reached the end
Your blog has helped me become a more positive and mindful person I am grateful for the transformative effect your words have had on me
This blog is like a breath of fresh air in the midst of all the negativity on the internet I’m grateful to have stumbled upon it
What other topics would you like to see covered on the blog? Let us know in the comments!
I simply could not go away your web site prior to suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard info a person supply on your guests? Is going to be back incessantly to investigate cross-check new posts.
Wow, wonderful blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is great, as well as the content!
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem along with your website in internet explorer, would test this텶E still is the market chief and a good section of other folks will pass over your magnificent writing due to this problem.
hello!,I like your writing very so much! proportion we keep up a correspondence extra approximately your post on AOL? I need an expert in this space to unravel my problem. May be that is you! Taking a look forward to see you.
Thanks, I have recently been looking for info about this subject for a while and yours is the greatest I have discovered so far. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the supply?
Thanks, I have recently been looking for info about this subject for a while and yours is the greatest I have discovered so far. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the supply?
I do agree with all the ideas you have introduced on your post. They are very convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are very short for newbies. May just you please prolong them a little from subsequent time? Thank you for the post.
I am not sure where you’re getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this information for my mission.
you are truly a just right webmaster. The site loading speed is incredible. It kind of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick. In addition, The contents are masterwork. you have done a great activity in this matter!
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue together with your site in internet explorer, would check this텶E still is the marketplace chief and a large element of other folks will leave out your magnificent writing due to this problem.
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to more added agreeable from you! By the way, how could we communicate?
I’ve read several just right stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot effort you place to create this kind of great informative website.
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this post is amazing, great written and include almost all significant infos. I would like to look extra posts like this.
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing. The clearness in your post is just nice and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Well with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work.
I’ve read several just right stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot effort you place to create this kind of great informative website.
Usually I do not read article on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very compelled me to take a look at and do it! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thank you, very nice article.
Usually I do not read article on blogs, however I would like to say that this write-up very compelled me to take a look at and do so! Your writing taste has been amazed me. Thanks, quite nice post.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike.
My brother suggested I might like this website. He was totally right. This post actually made my day. You cann’t imagine just how much time I had spent for this information! Thanks!
I just could not depart your web site prior to suggesting that I really loved the usual info an individual supply in your visitors? Is gonna be back regularly to check up on new posts.