Plants have been a crucial part of the earth’s ecosystem for millions of years. From towering trees to tiny mosses, they have diversified and adapted to various environments. One group of plants that has remained relatively unchanged for hundreds of millions of years is the Psilophyta, also known as whisk ferns. These fascinating plants are considered to be some of the simplest forms of vascular plants, and they hold a unique place in the evolution of plants.
Psilophyta
The Psilophyta are a group of primitive vascular plants that belong to the division Psilotophyta. They are known for their simple, unbranched stems and lack of true leaves and roots. Instead of leaves, they have small, scale-like appendages called “microphylls” that resemble tiny leaves. These microphylls are not used for photosynthesis, but rather, serve as structures for water uptake and gas exchange.

Whisk ferns are considered one of the earliest forms of vascular plants to colonize the land. They first appeared in the fossil record about 400 million years ago, and they have remained relatively unchanged since then.
Good to Know
- Oldest known vascular plants from the Silurian and Devonian periods.
- The division includes both fossil and living forms.
Where is Psilophyta found?
Psilotophyta, or whisk ferns, are usually found in damp, shady habitats such as forests, swamps, and bogs. They are commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions, but they can also be found in temperate areas. Whisk ferns have a cosmopolitan distribution and can be found on almost every continent, including North America, South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia. They are especially abundant in regions with high rainfall and high humidity, where they can grow in areas where other plants cannot survive.
Characteristics of Psilophyta
- The plant body is a rootless sporophyte that differentiates into a subterranean rhizome and an aerial erect shoot.
- Branching is dichotomous in both subterranean rhizome and aerial shoot.
- Leaves are usually small-scale-like.
- In the axis of the scale leaf, a specialized spore-bearing structure, ‘synangia’ are present.
- Spores are of equal sizes and shapes i.e., homosporous.
- The vascular cylinder is protostele.
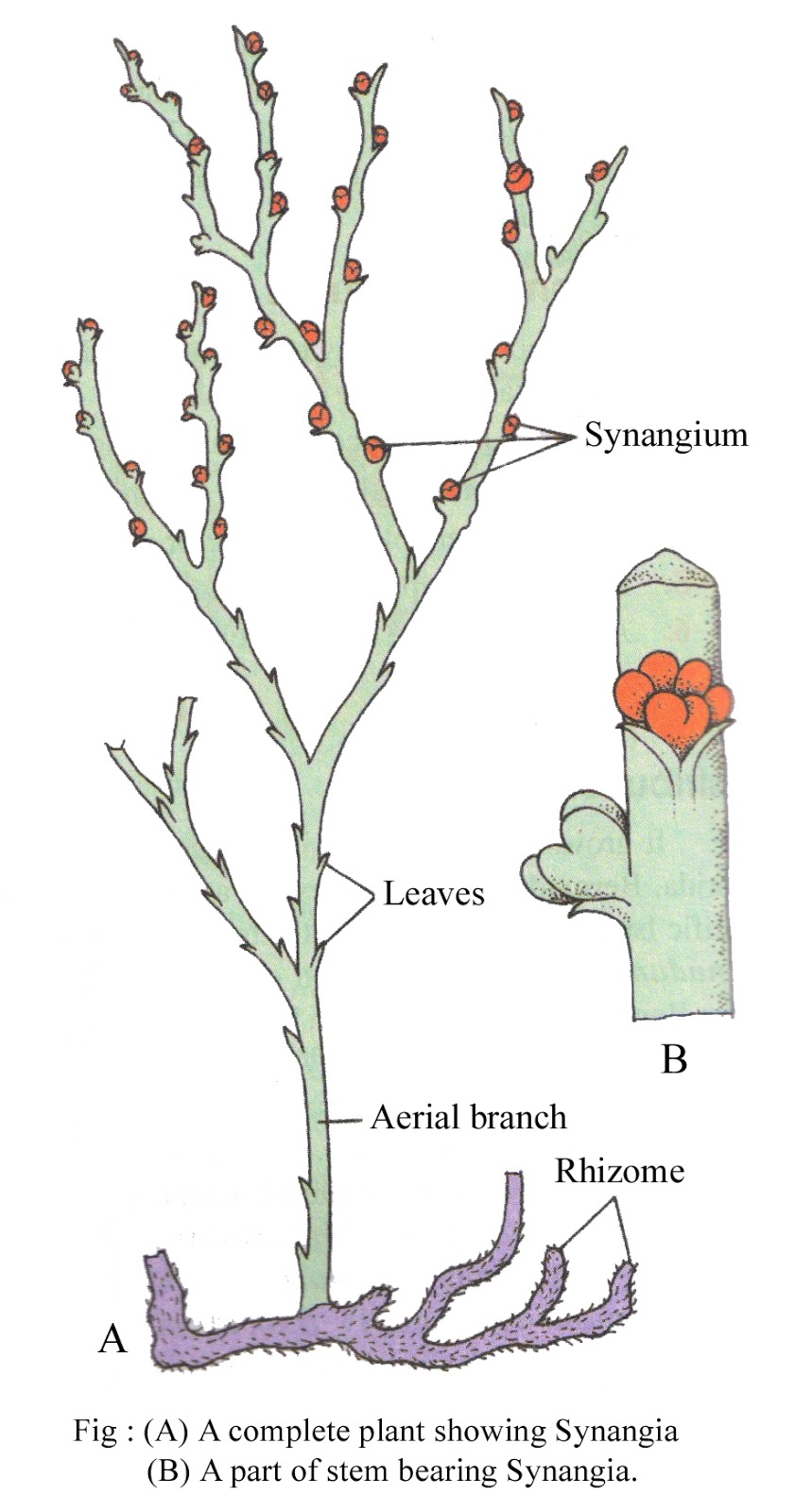
Structure of Psilophyta
- Simple Stems: Whisk ferns have simple, unbranched stems that are usually green and photosynthetic.
- Lack of True Leaves and Roots: Unlike most other vascular plants, whisk ferns lack true leaves and roots. Instead, they have small, scale-like structures called “microphylls” that resemble tiny leaves and serve as structures for water uptake and gas exchange.
- Rhizoids: Whisk ferns have small, root-like structures called rhizoids that anchor the plant to the soil and absorb water and nutrients.
- Sporangia: Whisk ferns produce spores called “sporangia” that contain the plant’s spores. These sporangia are often found at the tips of the stems and are surrounded by protective structures called “sporangiophores.”
- Life Cycle: Whisk ferns have a unique life cycle in which they produce both gametophytes (haploid plants) and sporophytes (diploid plants). The gametophytes are small and produce the male and female gametes, while the sporophytes are larger and produce the sporangia.
- Drought Tolerance: Due to their simple anatomy and ability to store water in their stems, whisk ferns are highly tolerant of drought and can survive in areas where other plants cannot.
- Ancient Evolution: Whisk ferns are one of the earliest forms of vascular plants to colonize land, and they have remained relatively unchanged for hundreds of millions of years. They are considered to be living fossils and provide valuable insights into the evolution of plants.

Structure of Psilophyta. Source: Biologyboom Psilophyta Examples
There are two main genera of whisk ferns: Psilotum and Tmesipteris.
- Psilotum: Psilotum is a genus of whisk ferns that contains about three species. The most common species is Psilotum nudum, also known as the naked whisk fern. It is found in tropical and subtropical regions and is characterized by its simple, unbranched stems and lack of leaves.

Psilotum. Source: Wikipedia - Tmesipteris: Tmesipteris is a genus of whisk ferns that contains about ten species. The species are found in tropical and subtropical regions and are characterized by their simple, unbranched stems and the presence of small, scale-like leaves called “microphylls.”
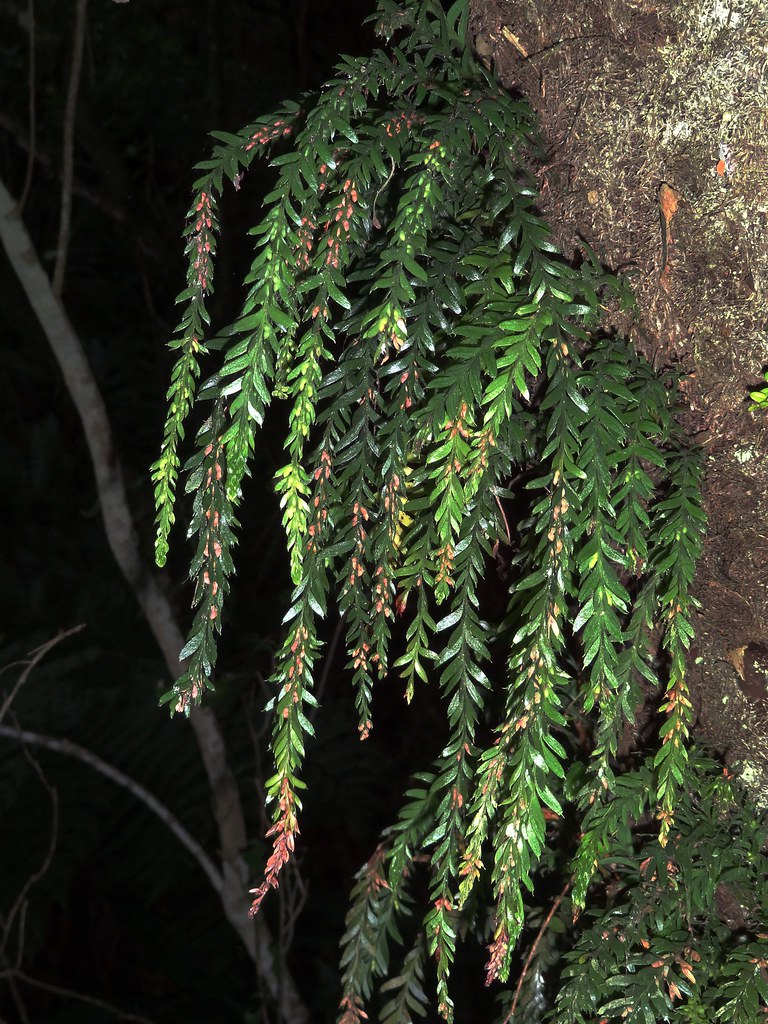

Tmesipteris. Source: Flickr These are just two examples of the genera of whisk ferns, but there are many other species and genera that belong to the Psilotophyta. These plants are considered to be living fossils, and they provide valuable insights into the evolution of plants and the history of life on earth.

Psilotum nudum. Source: biologie.uni-hamburg - Psilotum: Psilotum is a genus of whisk ferns that contains about three species. The most common species is Psilotum nudum, also known as the naked whisk fern. It is found in tropical and subtropical regions and is characterized by its simple, unbranched stems and lack of leaves.
 Plantlet The Blogging Platform of Department of Botany, University of Dhaka
Plantlet The Blogging Platform of Department of Botany, University of Dhaka




Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated
Every time I visit your site, I leave feeling more knowledgeable.
Just wish to say your article is as surprising The clearness in your post is just cool and i could assume youre an expert on this subject Fine with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post Thanks a million and please keep up the enjoyable work
Fantastic read! I was especially impressed by the depth provided on the topic, offering a perspective I hadn’t considered. Your insight adds significant value to the conversation. For future articles, it would be fascinating to explore more to dive deeper into this subject. Could you also clarify more about the topic? It caught my interest, and I’d love to understand more about it. Keep up the excellent work!
Fantastic site Lots of helpful information here I am sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious And of course thanks for your effort